A tendon is a thick fibrous band of connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. The Achilles tendon is located at the rear of the leg and connects the calf muscles to the foot. This tendon will allow for stretch and recoil of the calf muscles and will also transmit force between the muscles and foot.
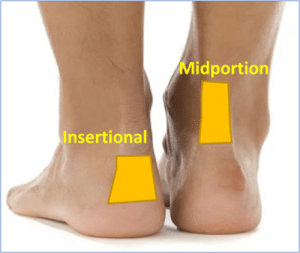
Achilles tendinopathy often presents with pain in either the mid-portion, or insertion of the tendon at the heel and it is painful to touch. There may also be thickening in the tendon.
Evidence suggests there are two main stages of the disease: a reactive stage and a degenerative stage, all with varying symptoms.
Cauze
The most common cause of an Achilles Tendinopathy is overloading the tendon, which can occur in people of all ages. Other causes can include:
- Să fii supraponderal
- O schimbare bruscă a nivelului de activitate
- Erorile de antrenament (alergare excesivă la deal, lipsă de condiționare)
- Side effects of certain medications e.g fluroquinolone antibiotics
- Boli sistemice, cum ar fi artrita reumatoidă, diabetul, hipertensiunea arterială, colesterolul ridicat.
- Hormonal changes i.e. Post menopause
- Consumul moderat de alcool
Simptome
Symptoms will vary dependent on its stage:
Reactive—an acute stage, where the Achilles can be constantly painful and wake you at night. There can also be swelling around the tendon. This needs to be managed by avoiding activities which aggravate the pain and using ice to help it settle.
Degenerative— this is the chronic stage where the tendon is no longer acutely painful, but the tendon healing has plateaued. This stage will require a loading exercise programme.
Tratament
There are some treatments that you can do for both insertional and mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy.
Stil de viață
Managing weight is important, therefore a balanced healthy diet is encouraged. This will aid your recovery and long-term health. Moderate alcohol use is a risk factor for Achilles tendinopathy.
Pain-Management
It not uncommon for your Achilles to be painful. Avoiding activity all together is not recommended in the long term. Do not be alarmed if your Achilles aches after exercise, this is to be expected. Medication such as ibuprofen might interfere with the body’s ability to repair the tendon so paracetamol is preferred. An ice pack can help but be careful not to put ice or heat packs directly on the skin – wrap them with a tea towel cover.
Modificarea activității
Activity is encouraged although adaptation is important. At times high impact activities might need to be scaled back to introduce activities that allow your tendon to recover but keep you active. Monitoring step count or intensity of walking are ways to modify your activity.
Ridicări de călcâi sau cupă
A heel lift is designed to offer cushion and reduce the pull of the Achilles tendon This has be shown to help some patients in recovery. Place this at the base of the heel inside your shoes.
Încălțăminte
Generally, avoiding footwear that aggravates your symptoms is advised. However, we need to be careful about this as sometimes the shoes might not be the aggravator it might simply be the task you’re doing. We advise wearing a practical, cushioned, stable shoe with a 8-10mm heel support, (such as running trainers or walking shoes) avoid flat and unsupportive options.
A running trainer is recommended in the recovery of your foot pain and is likely to assist in the symptom reduction phase. Avoiding dress shoes, hard heeled shoes, or backs of shoes that aggravate your symptoms. Often using Achilles heel protectors can assist in symptom relief.
Heel Protectors – ShoeInsoles.co.uk
GelX Achilles Heel Protector (simplyfeet.co.uk)
Tălpi interioare / Orteze pentru picioare
Insoles and foot orthotics are not routinely recommended. In some instances, whereby the patient has failed to recover or a flatter foot posture and might benefit from further support. Some insoles will be more cushioned based i.e., with a soft heel lift or some will have more structure i.e., arch support. There is no one size fits all approach, but you can access these yourself online.
Exercițiu
These can help reduce the pain in the tendon and restore the functionality but will take time to implement. A lot of exercises can be done at home, although seek advice from a health professional if you are unsure.
The exercises programmes are slightly different for insertional and mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy.
Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy Loading
You may have been assessed by a clinician and this program is a framework to build on, exercises could be added or taken away accordingly.
Faza 1:
Everyone is different with timelines so do not worry if you spend longer in a phase.
Starea pacientului: Durere și dificultăți în toate activitățile
Obiectiv: Start to exercise, aim to offer some pain relief in the initial phase
The following exercises can help with pain in the initial phase, although progression onto stage 2 is advised if these are relatively easy. Start without weight but then introduce this to all three exercises.
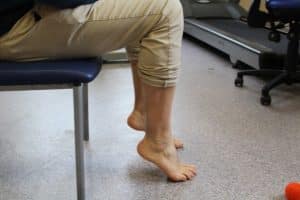
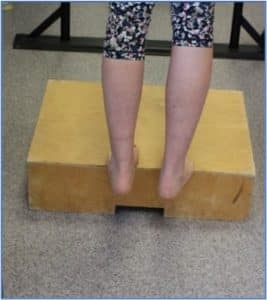
Phase 1: Seated Heel Raise Isometric Holds
- Sit with your knee bent at 90 degrees, foot flat to the floor
- Raise the heel (injured Achilles side) off the ground to full height. Slow and controlled movement is encouraged.
- Hold for 45 seconds, then slowly lower the heel to the ground, 2mins rest, 5 repetitions.
- Once this is doable to provide some further resistance place a heavy object on your knee (heavy textbook).

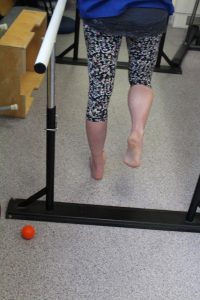
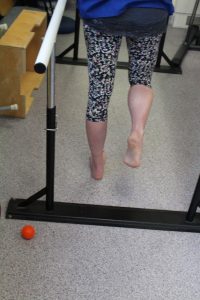
Phase 1: Standing Heel Raise Isometric Holds
- Using both feet raise the heels off the ground to full height. Slow controlled movement is encouraged.
- Hold for 45 seconds, then slowly lower the heel to the ground, 2mins rest, 5 repetitions.
- To add weight, place textbook or bag of potatoes in a backpack. Adding weight is important to provide greater resistance.
Phase 1: Standing Single heel raise Isometric
- Once double heel raise becomes comfortable, you can progress onto single leg exercise.
- Using just one leg (the injured Achilles) raise the heel off the ground to full height. Slow controlled movement is encouraged.
- Hold for 45 seconds, then slowly lower the heel to the ground.
- 2mins rest
- 5 repetitions
Faza 2
Starea pacientului: Pain has improved with phase 1 but still struggling with functional tasks move onto phase 2 loading
Obiectiv: Progress from phase 1. Now it’s time to push to discomfort and this can sometimes cause pain at the tendon- do not be concerned. If the pain has increased until the next day reduce some of the reps/sets appropriately
Phase 2: Seated Heel Raise
- Stați cu genunchiul îndoit la 90 de grade, cu picioarele sprijinite pe podea
- Ridicați încet ambele călcâie de la sol până la înălțimea maximă (ridicarea controlului)
- Țineți timp de 3 secunde, apoi coborâți încet la sol.
- 15 repetitions x 3 Daily.

Faza 2: Ridicarea călcâiului în picioare
- Stați pe ambele picioare și țineți-vă de un dulap sau de un scaun
- Ridicați încet ambele călcâie de la sol până la înălțimea maximă (ridicarea controlului)
- Țineți timp de 3 secunde, apoi coborâți încet la sol.
- 15 repetitions x 3 Daily.
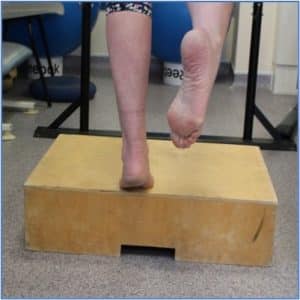
Phase 2: Eccentric heel raises- Flat surface
- Stați pe ambele picioare și țineți-vă de un dulap sau de un scaun
- Slowly raise both heels off the ground to mid to full height (control rising)
- Then transfer your weight onto the Achilles (painful leg) and slowly lower your heel to the ground.
- 15 repetări x 3 zilnic
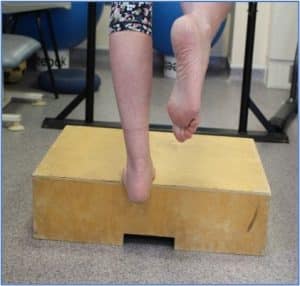
Phase 2: Single leg Standing Heel Raise
- Using just one leg the injured Achilles raise the heel off the ground to full height. Slow controlled movement is encouraged.
- Țineți timp de 3 secunde, apoi coborâți încet călcâiul la sol.
- 15 repetări x 3 zilnic
Faza 3
Patient status: Pain with exercise, morning stiffness, pain when performing heel raises
Goal: Strengthening and tissue adaptation
The following exercises can help build tolerance in the Achilles
Phase 3: Seated Heel Raise
- Phase 2 exercise but now with added weight i.e. backpack holding heavy books to provide further resistance
Phase 3: Eccentric heel raises-flat surface
- Phase 2 exercise but now with added weight i.e. backpack holding heavy books to provide further resistance
Phase 3: Single Leg Heel Raise
- Phase 2 exercise but now with added weight i.e. backpack holding heavy books to provide further resistance
Phase 3: Standing Heel Raise flat surface-Quick rebound
- Stand on both feet hold onto a sideboard or chair-aim is to do heel raises quickly
- Ridicați ambele călcâie de la sol la înălțimea maximă
- Coborâți la sol, apoi repetați ridicând din nou călcâiele de la sol.
- 20 de repetări x 3 zilnic
Faza 4
Starea pacientului: Handled the phase 3 exercise program, no pain in the tendon at the insertion towards the heel bone, possibly decreased or increased morning stiffness
Obiectiv: Heavier strength training, increase or start more physical activity. To do all phase 3 exercises as 1 set but 3 times with heavier load, 2-3 times/week
Mid-Portion Achilles Tendinopathy Loading
Faza 1
(Fiecare persoană are termene diferite, așa că nu vă faceți griji dacă petreceți mai mult timp într-o fază)
Starea pacientului: Durere și dificultăți în toate activitățile
Următoarele exerciții pot ajuta la atenuarea durerii în faza inițială, deși este recomandată trecerea la etapa 2 dacă acestea sunt relativ ușoare.
Phase 1: Seated Heel Raise Isometric Holds
- Sit with your knee bent at 90 degrees, foot flat to the floor
- Raise the heel (injured Achilles side) off the ground to full height. Slow and controlled movement is encouraged.
- Hold for 45 seconds, then slowly lower the heel to the ground, 2mins rest, 5 repetitions.

Phase 1: Standing Heel Raise Isometric Holds
- Using both feet raise the heels off the ground to full height. Slow controlled movement is encouraged.
- Hold for 45 seconds, then slowly lower the heel to the ground, 2mins rest, 5 repetitions.
Phase 1: Standing Single heel raise Isometric
- Once double heel raise becomes comfortable, you can progress onto single leg exercise standing up.
- Using just one leg (the injured Achilles) raise the heel off the ground to full height. Slow controlled movement is encouraged.
- Hold for 45 seconds, then slowly lower the heel to the ground, 2mins rest, 5 repetitions.
Faza 2
Starea pacientului: Pain has improved with phase 1 but still struggling with functional tasks move onto phase 2 loading
Obiectiv: Progressed from phase 1. Now time to push to discomfort and this can sometimes cause pain at the tendon- do not be concerned. If the pain has increased until the next day reduce some of the reps/sets appropriately.
Phase 2: Seated Heel Raise
- Stați cu genunchiul îndoit la 90 de grade, cu picioarele sprijinite pe podea
- Ridicați încet ambele călcâie de la sol până la înălțimea maximă (ridicarea controlului)
- Țineți timp de 3 secunde, apoi coborâți încet la sol.
- 15 repetări x 3 zilnic
Faza 2: Ridicarea călcâiului în picioare
- Stați pe ambele picioare și țineți-vă de un dulap sau de un scaun
- Ridicați încet ambele călcâie de la sol până la înălțimea maximă (ridicarea controlului)
- Țineți timp de 3 secunde, apoi coborâți încet la sol.
- 15 repetări x 3 zilnic
Phase 2: Eccentric heel raises- Flat surface
- Stați pe ambele picioare și țineți-vă de un dulap sau de un scaun
- Slowly raise both heels off the ground to mid to full height (control rising)
- Then transfer your weight onto the Achilles (painful leg) and slowly lower your heel to the ground.
- 15 repetări x 3 zilnic
Faza 2: Ridicarea călcâiului în picioare cu un singur picior
- Using just one leg the injured Achilles raise the heel off the ground to full height. Slow controlled movement is encouraged.
- Țineți timp de 3 secunde, apoi coborâți încet călcâiul la sol.
- Repetați de 5 ori.
- To add weight place textbook or bag of potatoes in a backpack. Adding weight is important to provide greater resistance.
Faza 3
Starea pacientului: Pain with exercise, morning stiffness, pain when performing heel raises
Obiectiv: Strengthening and tissue adaptation
The following exercises can help build tolerance in the Achilles
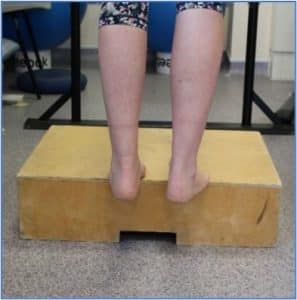
Phase 3: Standing Heel Raise on a Step
- În picioare pe scări, ridicați-vă pe vârful picioarelor pe ambele picioare
- Coborâți încet ambele tocuri sub scări cu 2-3 cm, întinzând mușchii picioarelor din spate
- Repetați ridicându-vă din nou pe vârfurile picioarelor cu control
- 15 repetări x 3 zilnic
Phase 3: Eccentric heel raises on a Step
- În picioare pe scări, ridicați-vă pe vârful picioarelor pe ambele picioare
- Transfer weight onto your (injured leg) slowly lowering the heel below the stairs 2-3cm.
- If you have it both legs do one leg, then the other
- 15 repetări x 3 zilnic
Phase 3: Single Leg Heel Raise on a Step
- Standing on the stairs using on leg raise up onto your tip toes
- Then slowly drop the heel about 2-3cm below the step, feel a stretch in the back of the leg.
- Then repeat moving back onto your toes with the heel at full height
- 15 Repetitions x3 Daily
Phase 3: Standing Heel Raise flat surface-Quick rebound
- Stand on both feet hold onto a sideboard or chair-aim is to do heel raises quickly
- Ridicați ambele călcâie de la sol la înălțimea maximă
- Coborâți la sol, apoi repetați ridicând din nou călcâiele de la sol.
- 20 de repetări x 3 zilnic
Phase 3: Seated Heel Raise
- Stați cu genunchiul îndoit la 90 de grade, cu picioarele sprijinite pe podea
- Ridicați încet ambele călcâie de la sol până la înălțimea maximă (ridicarea controlului)
- Țineți timp de 3 secunde, apoi coborâți încet la sol.
- 15 repetări x 3 zilnic

Faza 4
Starea pacientului: Handled the phase 3 exercise program, no pain in tendon where it attaches to the heel bone, possibly decreased or increased morning stiffness.
Obiectiv: Antrenament de forță mai intens, creșterea sau începerea unei activități fizice mai intense
To do all exercises at 1 set but 3 times a day and with heavier load, 2-3 times a week. This could be a backpack with books in on your back
Phase 4: Single Leg Heel Raise on a Step
- Phase 3 exercise but now with added weight i.e backpack add heavy books to provide further resistance.
Phase 4: Eccentric heel raises on a Step
- See phase 3 exercise but now with added weight i.e backpack add heavy books to provide further resistance
Faza 4: Ridicarea călcâiului în picioare - suprafață plană - revenire rapidă
- See phase 3 exercise but now with added weight i.e backpack add heavy books to provide further resistance
Phase 4: Seated Heel Raises
- See phase 3 exercise but now with added weight i.e add heavy book on top of your knee to provide further resistance
Phase 5
Starea pacientului: Minimal symptoms, morning stiffness not every day, can participate in sports without difficulty
Obiectiv: Maintenance exercise, no symptoms
Perform these exercises 3 times a week instead of daily and see phase 4 for instructions.
Phase 5: Single Leg Heel Raise on a Step
Phase 5: Eccentric heel raises on a Step
Phase 5: Standing Heel Raise flat surface-Quick rebound
Warning
It is normal to feel some discomfort, but do not push yourself to the point where you’re in pain for 12 hours or more. Be very careful with any activity you do and pace your return to exercise. Pain is the warning sign; don’t ignore it.
You should expect mild – moderate pain that stops with rest. Do not continue if pain persists all day
Shockwave Treatment
Terapia cu unde de șoc extracorporeale radiale (ESWT) este un tratament neinvaziv care implică trecerea undelor de presiune de înaltă energie în țesutul afectat pentru a crește fluxul sanguin și a stimula repararea. Organismul răspunde la undele de șoc prin creșterea circulației sângelui și a metabolismului în zona afectată, ceea ce se crede că accelerează procesele proprii de vindecare ale organismului. Dovezile arată că poate ajuta în tratamentul tendinopatiilor cronice atunci când este utilizat alături de alte forme de tratament conservator, cum ar fi exercițiile fizice, scăderea în greutate și analgezicele.
Management chirurgical
This can involve surgical debridement of the tendon with removal for abnormal tissue and allow the tissue to repair. Sometimes a gastrocnemius release is performed to reduce tendon tension.
Există riscuri în chirurgia piciorului și gleznei (acestea se pot extinde atunci când se face clic pe ele)
În afara muncii Va exista o cerință de a ridica piciorul și de a vă odihni fără a purta greutăți, apoi cu semi-greutate.
Umflături și rigiditate- Piciorul se poate umfla ca răspuns la intervenția chirurgicală și ca parte a procesului de vindecare. În unele cazuri, umflarea poate dura până la șase luni pentru a se retrage complet. Deși, în unele cazuri, după intervenția chirurgicală, piciorul poate prezenta o rigiditate crescută.
Infecție- Intervenția chirurgicală este invazivă, ceea ce reprezintă și un risc de infecție. În unele cazuri, aceasta poate întârzia vindecarea și va necesita tratament cu antibiotice.
Cheaguri de sânge- Există un risc scăzut de apariție a unui cheag de sânge după operația la picior. Urmarea sfaturilor pre și post operatorii va contribui la reducerea acestui risc.
Amorțeală- Poate exista în zona chirurgicală dacă a existat o întrerupere a unui nerv.
Sindromul durerii regionale cronice Chirurgia poate duce uneori la umflarea, durerea și sensibilitatea ridicată a piciorului. Acest lucru poate fi dificil de gestionat și adesea pacienții vor fi trimiși la clinica durerii pentru sprijin.
Dacă vă chinuiți să vă gestionați afecțiunea piciorului?
Contactați medicul de familie dacă aveți nevoie de mai mult ajutor și îndrumare; în unele cazuri, este necesară o trimitere la serviciile musculo-scheletice locale, care vă pot sfătui cu privire la tratamentul adecvat sau la căile de acces potrivite pentru dumneavoastră.
Înapoi la picior și gleznă